Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
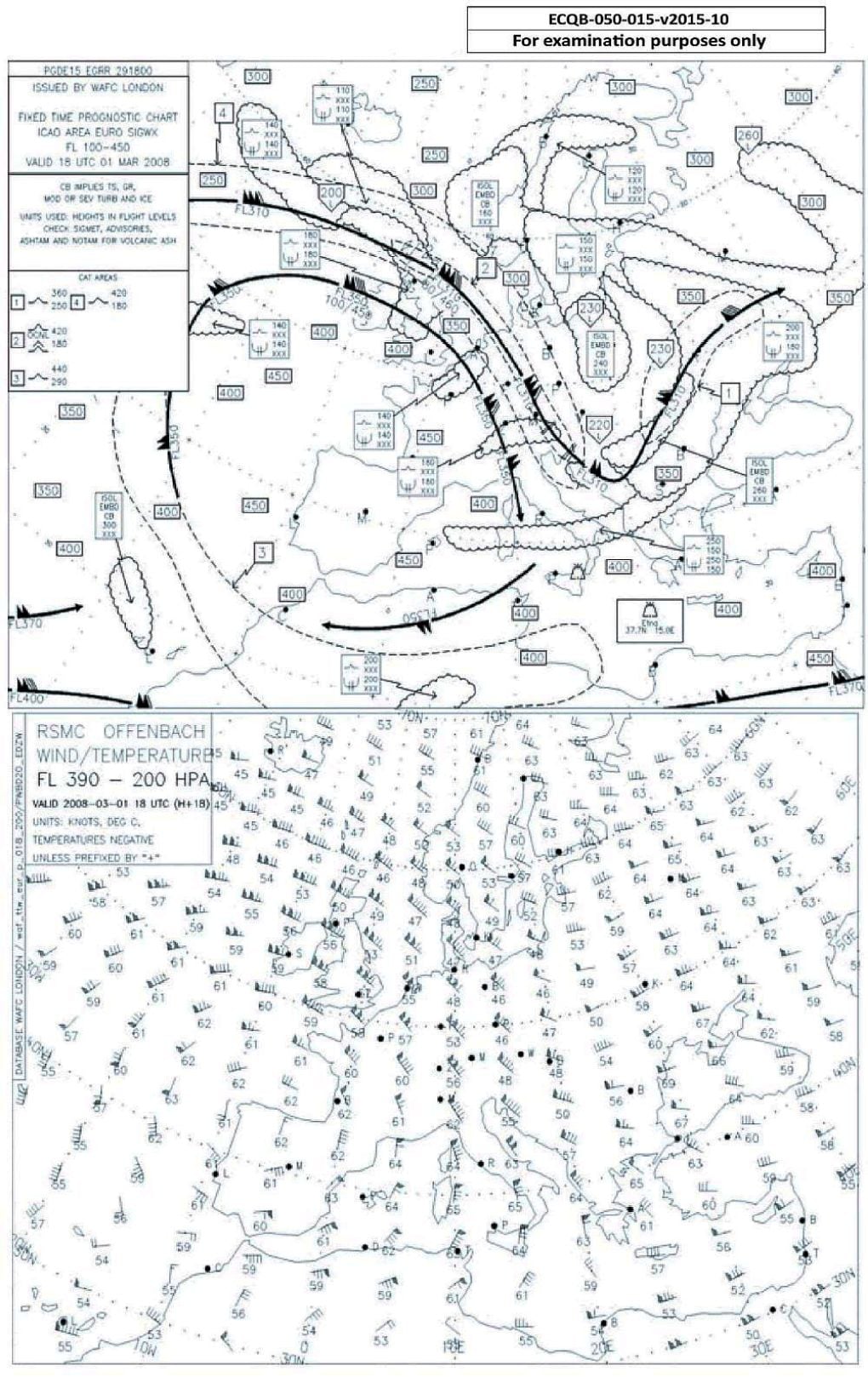
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Übungstest schaltet alle Online-Simulator-Fragen frei
Vielen Dank, dass du dich für die kostenlose Version des CPL(A) Modular - MeteorologiePraxistests entschieden hast! Vertiefe dein Wissen über CPL(A) Modular Simulator weiter; Indem du die Vollversion unseres CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulators freischaltest, kannst du Tests mit über 1232 ständig aktualisierten Fragen absolvieren und deine Prüfung problemlos bestehen. 98% der Personen bestehen die Prüfung im ersten Versuch, nachdem sie sich mit unseren 1232 Fragen vorbereitet haben.
KAUFE JETZTWas kannst du von unseren CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Übungstests erwarten und wie bereitest du dich auf eine Prüfung vor?
Die CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator-Übungstests sind Teil der CPL(A) Modular Datenbank und bieten die beste Möglichkeit, sich auf jede CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie-Prüfung vorzubereiten. Die CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Übungstests bestehen aus 1232 Fragen, die in 10 Themen unterteilt sind, und wurden von Experten verfasst, um dir zu helfen und dich darauf vorzubereiten, die Prüfung beim ersten Versuch zu bestehen. Die CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Datenbank enthält Fragen aus früheren und anderen Prüfungen, sodass du üben kannst, vergangene und zukünftige Fragen zu simulieren. Die Vorbereitung mit dem CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator gibt dir auch eine Vorstellung davon, wie viel Zeit du benötigst, um jeden Abschnitt des CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Übungstests abzuschließen. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass der CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator die klassischen CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Studienführer nicht ersetzt; Der Simulator bietet jedoch wertvolle Einblicke in das, was dich erwartet und wie viel du arbeiten musst, um dich auf die CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie-Prüfung vorzubereiten.
KAUFE JETZTDer CPL(A) Modular - MeteorologieÜbungstest stellt daher zusammen mit unserem CPL(A) Modular Übungstest ein hervorragendes Tool dar, um sich auf die eigentliche Prüfung vorzubereiten. Unser CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator hilft dir, deinen Vorbereitungsstand einzuschätzen und deine Stärken und Schwächen zu verstehen. Unten kannst du alle Quiz lesen, die du in unserem CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator findest, und wie unsere einzigartige CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Datenbank aus echten Fragen besteht:
Info-Quiz:
- Quizname:CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie
- Gesamtzahl der Fragen:1232
- Anzahl der Fragen für den Test:100
- Bestehendes Ergebnis:70%
- Anzahl der Themen:10 Themen
- Air Masses And Fronts:130 Fragen
- Climatology:85 Fragen
- Clouds And Fog:143 Fragen
- Flight Hazards:149 Fragen
- Meteorological Information:176 Fragen
- Precipitation:31 Fragen
- Pressure Systems:62 Fragen
- The Atmosphere:208 Fragen
- Thermodynamics:33 Fragen
- Wind:215 Fragen
Mit unserer mobilen App kannst du dich auf die CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie-Prüfungen vorbereiten. Sie ist sehr einfach zu bedienen und funktioniert bei einem Netzwerkausfall sogar offline, mit allen Funktionen, die du zum Lernen und Üben mit unserem CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator benötigst.
Verwende unsere mobile App, die sowohl für Android- als auch für iOS-Geräte verfügbar ist, mit unserem CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Simulator. Du kannst es überall verwenden und denke immer daran, dass unsere mobile App kostenlos und in allen Geschäften verfügbar ist.
Unsere mobile App enthält alle CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie Übungstests, die aus 1232 Fragen bestehen, die nach 10 Themen unterteilt sind, und bieten außerdem Lernmaterial, um die Abschlussprüfung CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie mit garantiertem Erfolg zu bestehen. Unsere CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie-Datenbank enthält Hunderte von Fragen und CPL(A) Modular Tests im Zusammenhang mit der CPL(A) Modular - Meteorologie-Prüfung. Auf diese Weise kannst du überall üben, auch offline ohne Internet.
KAUFE JETZT