Test
Test
EDDM 250850Z 33005KT 1400 R26R/P1500N R26L/1500N BR SCT002 OVC003 05/05 Q1025 NOSIG
Which of the following statements is correct?
1
2
3
4
Test
1
2
3
4
Test
Test
Test
Test
Over Palma de Mallorca at what flight level would you expect to find the tropopause according to the chart?
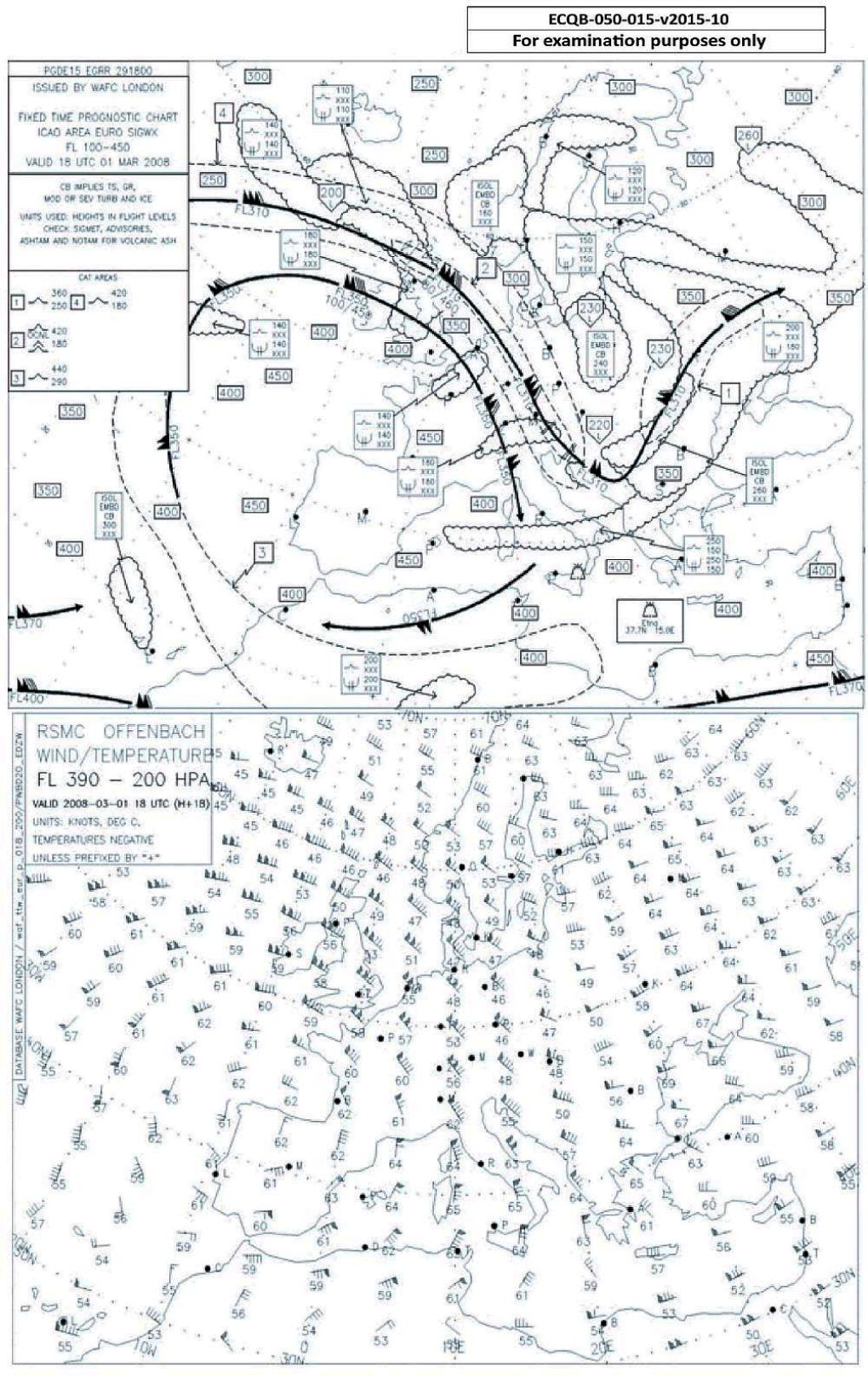
Test
1
2
3
4
Test
1
2
3
4
Test
1
2
3
4
Test PPL (A) Meteorology Los test de práctica desbloquean todas las preguntas del simulador online
¡Gracias por elegir la versión gratis de prueba de práctica test de Test PPL (A) Meteorology ! Profundiza aún más tus conocimientos con Simulador de Examen Licencia PPL Avión; desbloqueando la versión completa de nuestro simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology podrás hacer test con más de 1232 preguntas actualizadas constantemente y aprobar fácilmente tu examen. El 98% de la gente aprueba el examen a la primera después de prepararse con nuestras 1232 preguntas.
COMPRAR AHORA¿Qué esperar de nuestros Test PPL (A) Meteorology test de práctica y cómo prepararte para cualquier examen?
Los test de práctica Test PPL (A) Meteorology del simulador son parte de la Examen Licencia PPL Avión Base de datos y son la mejor manera de prepararse para cualquier examen de Test PPL (A) Meteorology. Los test de práctica de Test PPL (A) Meteorology consisten en 1232 preguntas divididas por 10 temas y están escritas por expertos para ayudarte a aprobar el examen en el primer intento. La base de datos de Test PPL (A) Meteorology incluye preguntas de exámenes anteriores, lo que significa que podrás practicar preguntas anteriores y futuras. La preparación con el simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology te dará también una idea del tiempo que te llevará completar cada sección de los test de práctica de Test PPL (A) Meteorology . Es importante saber que el Simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology no reemplaza las clásicas guías de estudio de Test PPL (A) Meteorology ; aún así, el Simulador ofrece información útil sobre qué esperar y cuánto tendrás que practicar para estar preparado para el día del examen de Test PPL (A) Meteorology .
COMPRAR AHORALos test de práctica de Test PPL (A) Meteorology representan una excelente herramienta para prepararte para el examen real junto con nuestros test de práctica de Examen Licencia PPL Avión . Nuestro Simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology te ayudará a evaluar tu nivel de preparación y a entender tus fortalezas y debilidades. Abajo puedes leer todos los test que encontrarás en nuestro simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology y cómo nuestra base de datos de Test PPL (A) Meteorology compone preguntas reales:
Información del test:
- Nombre del test:Test PPL (A) Meteorology
- Número total de preguntas:1232
- Número de preguntas para el test:100
- Puntuación de aprobado:70%
- Número de temas:10 Temas
- Air Masses And Fronts:130 Preguntas
- Climatology:85 Preguntas
- Clouds And Fog:143 Preguntas
- Flight Hazards:149 Preguntas
- Meteorological Information:176 Preguntas
- Precipitation:31 Preguntas
- Pressure Systems:62 Preguntas
- The Atmosphere:208 Preguntas
- Thermodynamics:33 Preguntas
- Wind:215 Preguntas
Puedes prepararte para los exámenes de Test PPL (A) Meteorology con nuestra aplicación móvil. Es muy fácil de usar e incluso funciona sin conexión a internet, con todas las funciones que necesitas para estudiar y practicar con nuestro Simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology .
Usa nuestra aplicación móvil, disponible para dispositivos Android e iOS, con nuestro Simulador de Test PPL (A) Meteorology . Puedes usarla donde quieras y recuerda siempre que nuestra app es gratis y disponible en todas las App Stores.
Nuestra aplicación móvil contiene todos los test de práctica de Test PPL (A) Meteorology que consisten en 1232 preguntas divididas por 10 temas y también ofrecen material de estudio para aprobar el examen final Test PPL (A) Meteorology con éxito garantizado.
COMPRAR AHORA