Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
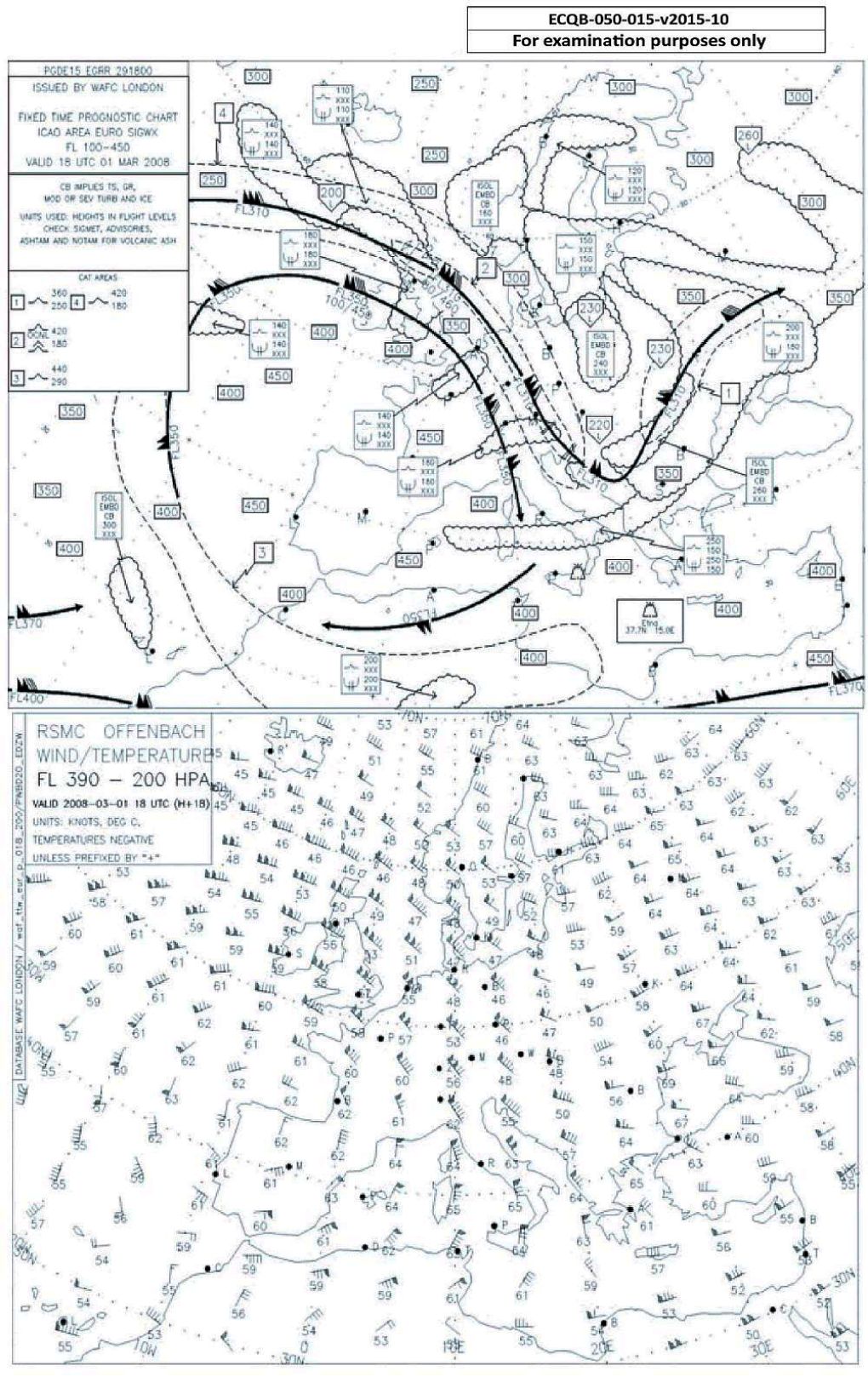
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz e Simulatore: Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology - sblocca tutte le domande del simulatore online
Grazie per aver scelto la versione free del Quiz Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology! Approfondisci ulteriormente le tue conoscenze con i nostri Simulatori Licenza LAPL Aereo; Sbloccando la versione completa del nostro Simulatore Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology potrai effettuare test e quiz con oltre 1232 domande sempre aggiornate e superare facilmente la tua prove d’esame. Il 98% di persone che si sono esercitate con le nostre 1232 domande hanno superato l'esame al primo tentativo.
ACQUISTA ORACosa aspettarsi dal nostro Simulatore Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology e come prepararsi a qualsiasi quiz Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology?
I Test pratici di Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology fanno parte della Banca Dati Licenza LAPL Aereo e rappresentano il modo migliore per prepararsi a qualsiasi esame per Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology. I quiz sono composti da 1232 domande divise per 10 argomenti e sono scritti da esperti per aiutarvi e prepararvi a raggiungere l’obiettivo di superare l’esame al primo tentativo. La banca dati per Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology include domande apparse in esami precedenti e non solo, il che significa che sarete in grado di esercitarvi simulando le domande passate e future. La preparazione al Test Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology vi offrirà anche un’idea del tempo necessario per completare ogni sezione del Quiz Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology. È importante notare che il Simulatore Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology non sostituisce le classiche guide Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology di studio; tuttavia, il Simulatore fornisce indicazioni preziose su cosa aspettarsi e su quanto lavoro occorra fare per prepararsi all'esame Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology.
ACQUISTA ORAI Quiz Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology rappresentano quindi un ottimo strumento per prepararsi all’esame vero e proprio assieme ai nostri Quiz Licenza LAPL Aereo. I nostri test ti aiuteranno a valutare il tuo livello di preparazione e a comprendere i tuoi punti di forza e debolezza. Di seguito potrai leggere tutti i quiz che troverai nel nostro Simulatore Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology e come è composta la nostra unica Banca Dati Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology fatta di domande vere e reali:
Info quiz:
- Nome del quiz:Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology
- Numero totale di domande:1232
- Numero di domande per il test:100
- Punteggio di superamento:70%
- Numero di argomenti:10 argomenti
- Air Masses And Fronts:130 domande
- Climatology:85 domande
- Clouds And Fog:143 domande
- Flight Hazards:149 domande
- Meteorological Information:176 domande
- Precipitation:31 domande
- Pressure Systems:62 domande
- The Atmosphere:208 domande
- Thermodynamics:33 domande
- Wind:215 domande
Potete prepararvi agli esami Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology anche con la nostra applicazione mobile. È molto facile da usare e funziona anche off-line in caso di mancata disponibilità di rete, con tutte le funzioni necessarie per studiare ed esercitarvi con la nostra
Utilizzate la nostra Applicazione Mobile, disponibile sia per Android che per iOS, con il nostro Simulatore Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology. Potete utilizzarla ovunque e ricordate sempre che la nostra applicazione mobile è gratuita e disponibile su tutti gli Store.
L’applicazione mobile contiene tutte i Quiz Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology per un totale di 1232 domande divisi per 10 argomenti e fornirà il materiale di studio per superare l’esame finale con un successo garantito. Le nostre Banche Dati Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology contengono centinaia di domande relative all'Esame Quiz LAPL (A) Meteorology e ai Test Licenza LAPL Aereo. In questo modo sarà possibile esercitarsi quando e dove volete anche in modalità offline.
ACQUISTA ORA