Quiz
Quiz
EDDM 250850Z 33005KT 1400 R26R/P1500N R26L/1500N BR SCT002 OVC003 05/05 Q1025 NOSIG
Which of the following statements is correct?
1
2
3
4
Quiz
1
2
3
4
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Quiz
Over Palma de Mallorca at what flight level would you expect to find the tropopause according to the chart?
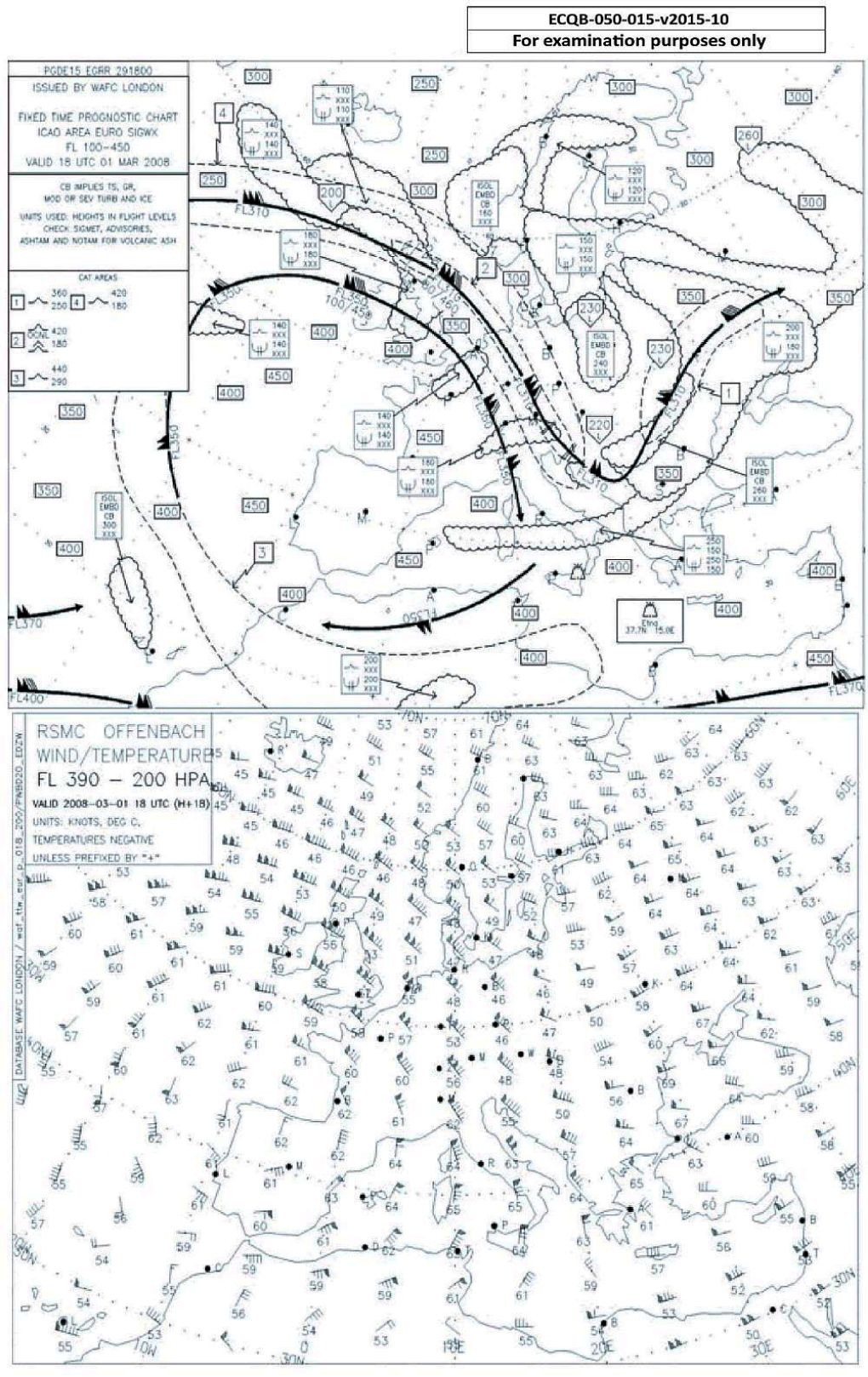
Quiz
1
2
3
4
Quiz
1
2
3
4
Quiz
1
2
3
4
CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Practice test unlocks all online simulator questions
Thank you for choosing the free version of the CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam practice test! Further deepen your knowledge on CPL - Commercial Pilot Licence Test for Aeroplanes Simulator; by unlocking the full version of our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator you will be able to take tests with over 1232 constantly updated questions and easily pass your exam. 98% of people pass the exam in the first attempt after preparing with our 1232 questions.
BUY NOWWhat to expect from our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam practice tests and how to prepare for any exam?
The CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator Practice Tests are part of the CPL - Commercial Pilot Licence Test for Aeroplanes Database and are the best way to prepare for any CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam exam. The CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam practice tests consist of 1232 questions divided by 10 topics and are written by experts to help you and prepare you to pass the exam on the first attempt. The CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam database includes questions from previous and other exams, which means you will be able to practice simulating past and future questions. Preparation with CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator will also give you an idea of the time it will take to complete each section of the CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam practice test . It is important to note that the CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator does not replace the classic CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam study guides; however, the Simulator provides valuable insights into what to expect and how much work needs to be done to prepare for the CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam exam.
BUY NOWCPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Practice test therefore represents an excellent tool to prepare for the actual exam together with our CPL - Commercial Pilot Licence Test for Aeroplanes practice test . Our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator will help you assess your level of preparation and understand your strengths and weaknesses. Below you can read all the quizzes you will find in our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator and how our unique CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Database made up of real questions:
Info quiz:
- Quiz name:CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam
- Total number of questions:1232
- Number of questions for the test:100
- Pass score:70%
- Number of topics:10 Topics
- Air Masses And Fronts:130 Questions
- Climatology:85 Questions
- Clouds And Fog:143 Questions
- Flight Hazards:149 Questions
- Meteorological Information:176 Questions
- Precipitation:31 Questions
- Pressure Systems:62 Questions
- The Atmosphere:208 Questions
- Thermodynamics:33 Questions
- Wind:215 Questions
You can prepare for the CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam exams with our mobile app. It is very easy to use and even works offline in case of network failure, with all the functions you need to study and practice with our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator.
Use our Mobile App, available for both Android and iOS devices, with our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Simulator . You can use it anywhere and always remember that our mobile app is free and available on all stores.
Our Mobile App contains all CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam practice tests which consist of 1232 questions that are divided by 10 topics and also provide study material to pass the final CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam exam with guaranteed success. Our CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam database contain hundreds of questions and CPL - Commercial Pilot Licence Test for Aeroplanes Tests related to CPL (A) - Meteorology Practice Exam Exam. This way you can practice anywhere you want, even offline without the internet.
BUY NOW